Welcome back to the Python Tutorial Series for Beginners! 🎉
In Lesson 2, we explored variables and data types in Python.
Now in Lesson 3, we’ll dive into Operators – the tools that allow us to perform calculations, compare values, and build logic in our programs.
By the end of this lesson, you’ll understand:
- Arithmetic operators (
+, -, *, /, etc.) - Comparison operators (
==, !=, >, <) - Logical operators (
and, or, not) - Assignment operators (
+=, -=, etc.)
🔹 What are Operators?
Operators are special symbols or keywords in Python used to perform operations on values and variables.
Think of them like the buttons on a calculator – but more powerful.
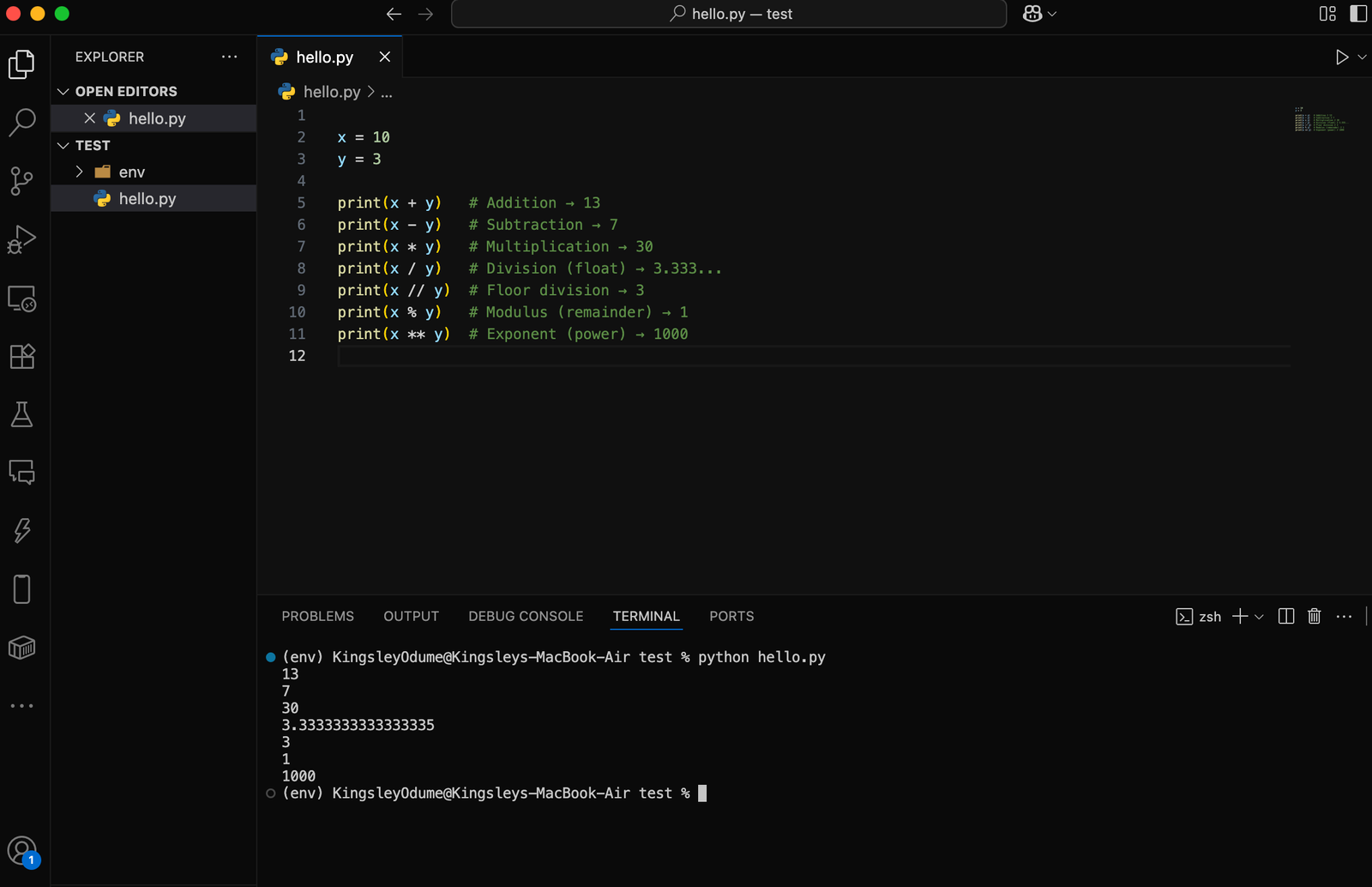
🔹 1. Arithmetic Operators
These are used to perform basic math operations:
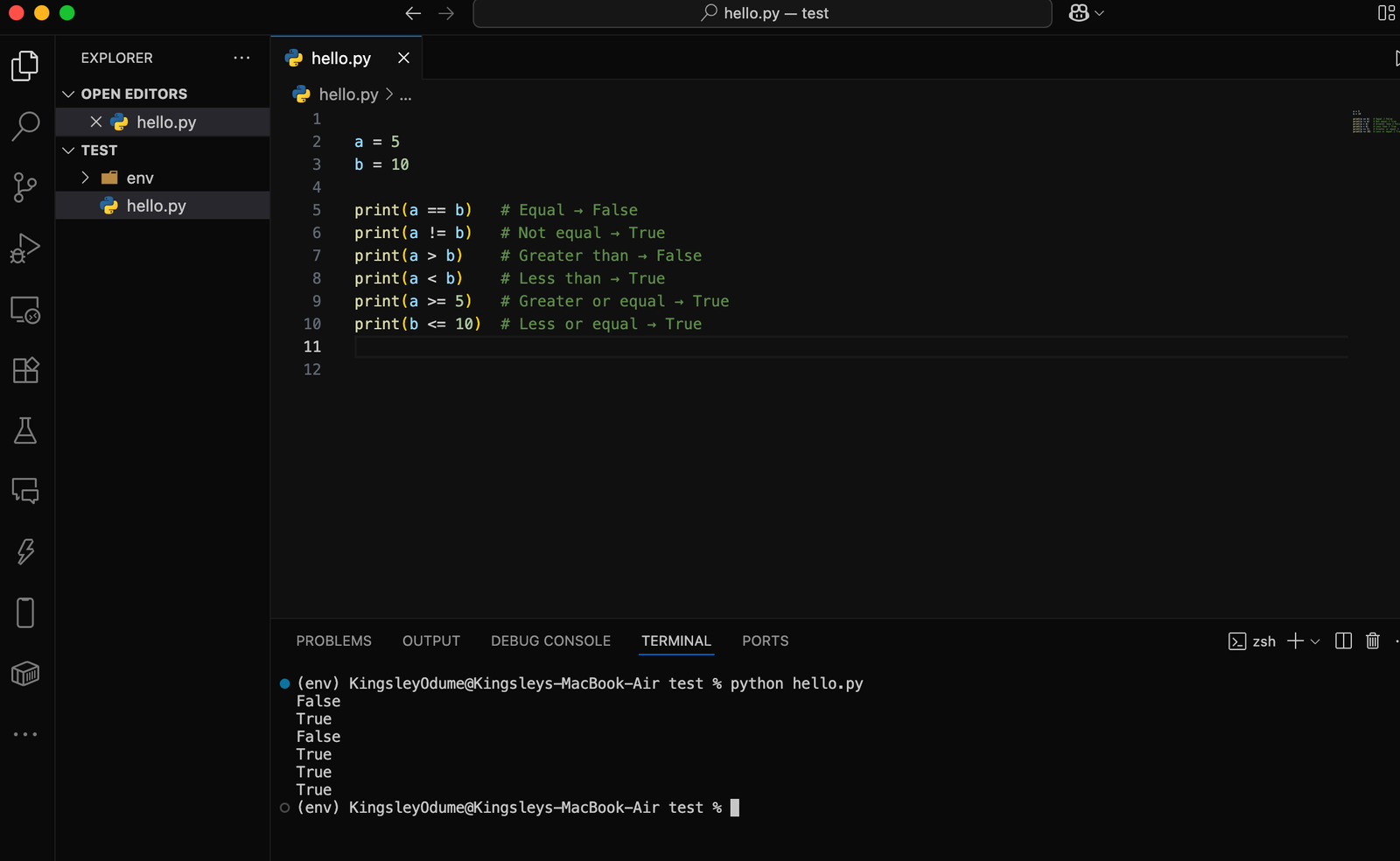
🔹 2. Comparison Operators
These are used to compare two values. They return True or False.
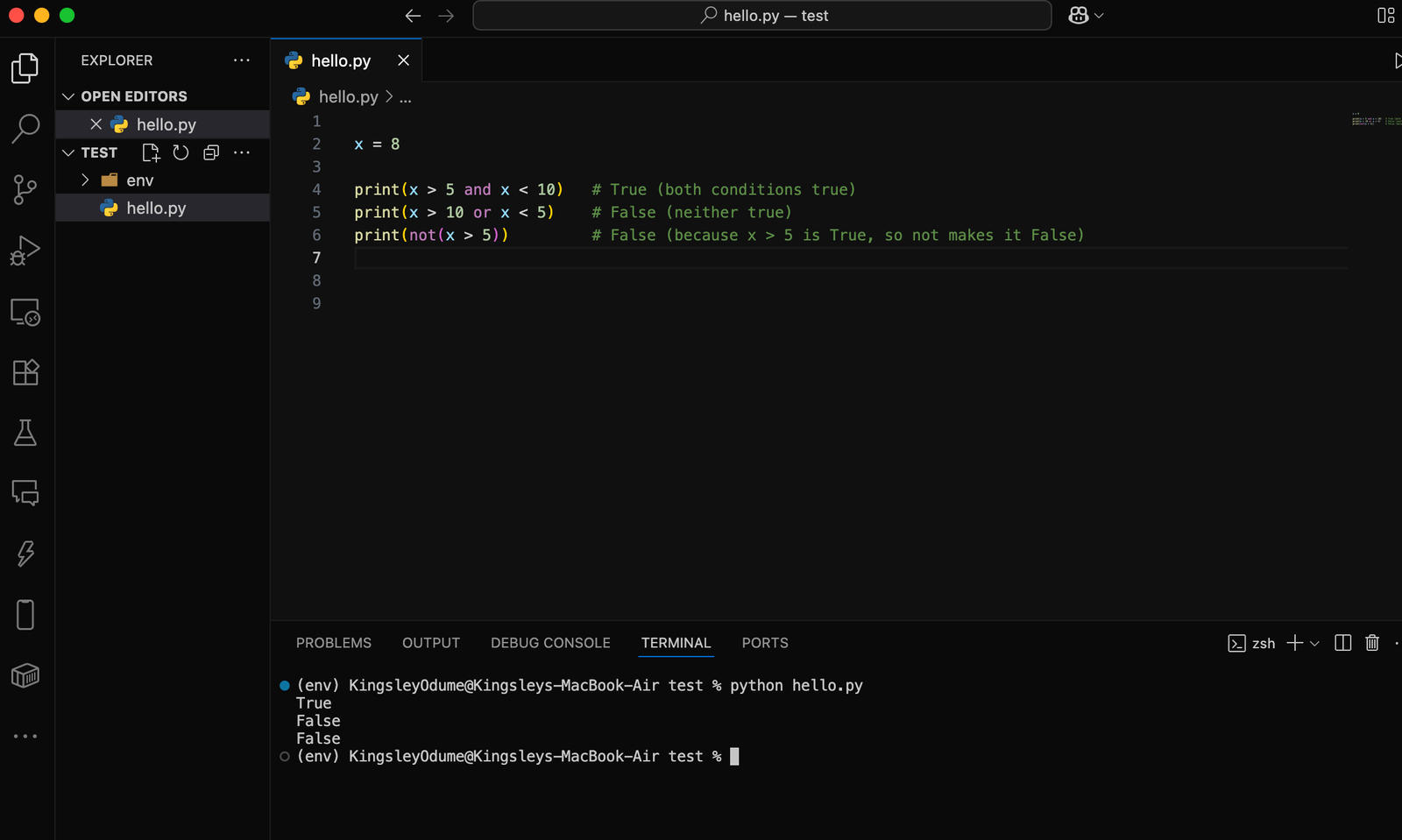
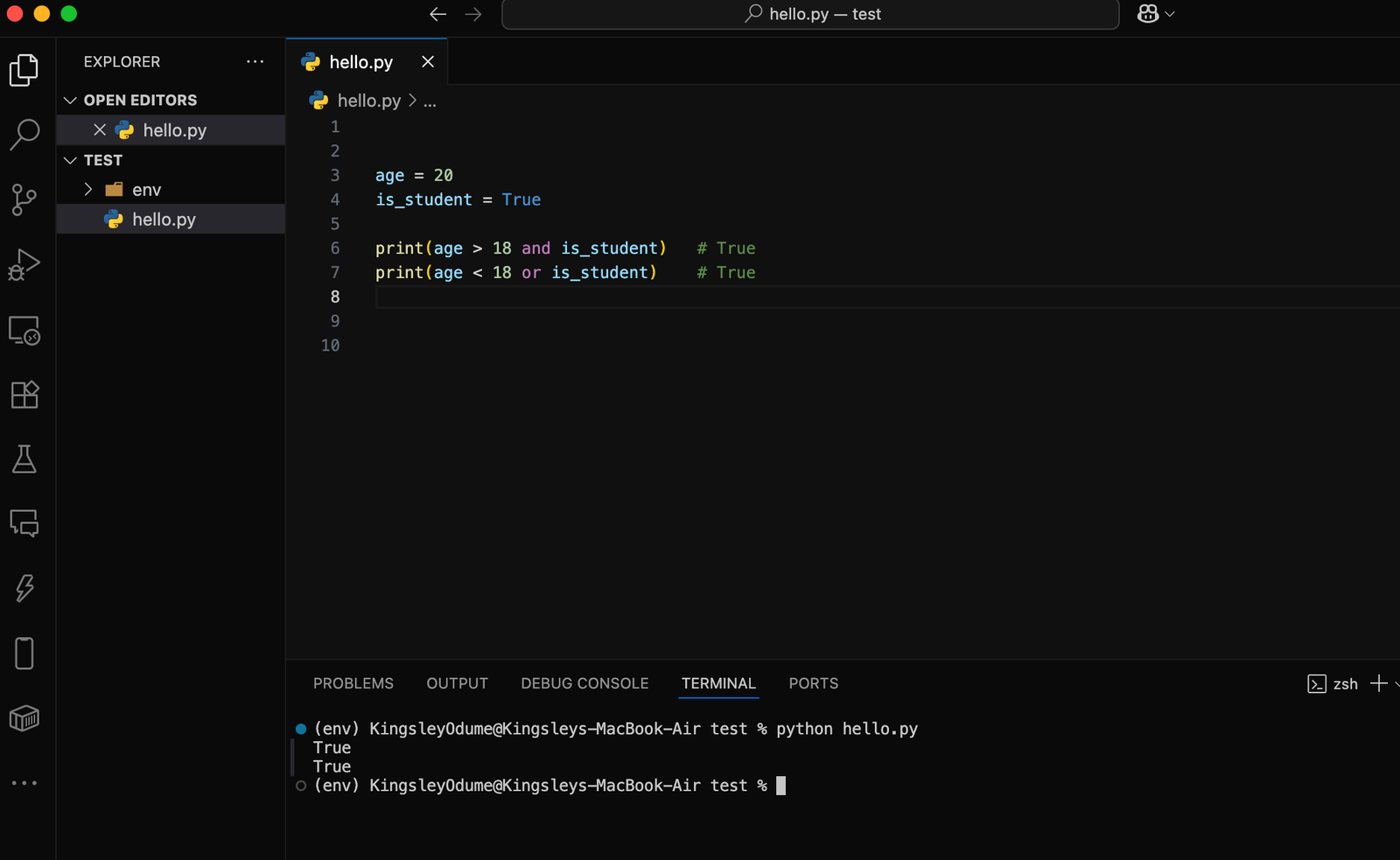
🔹 3. Logical Operators
Logical operators are used to combine conditions.
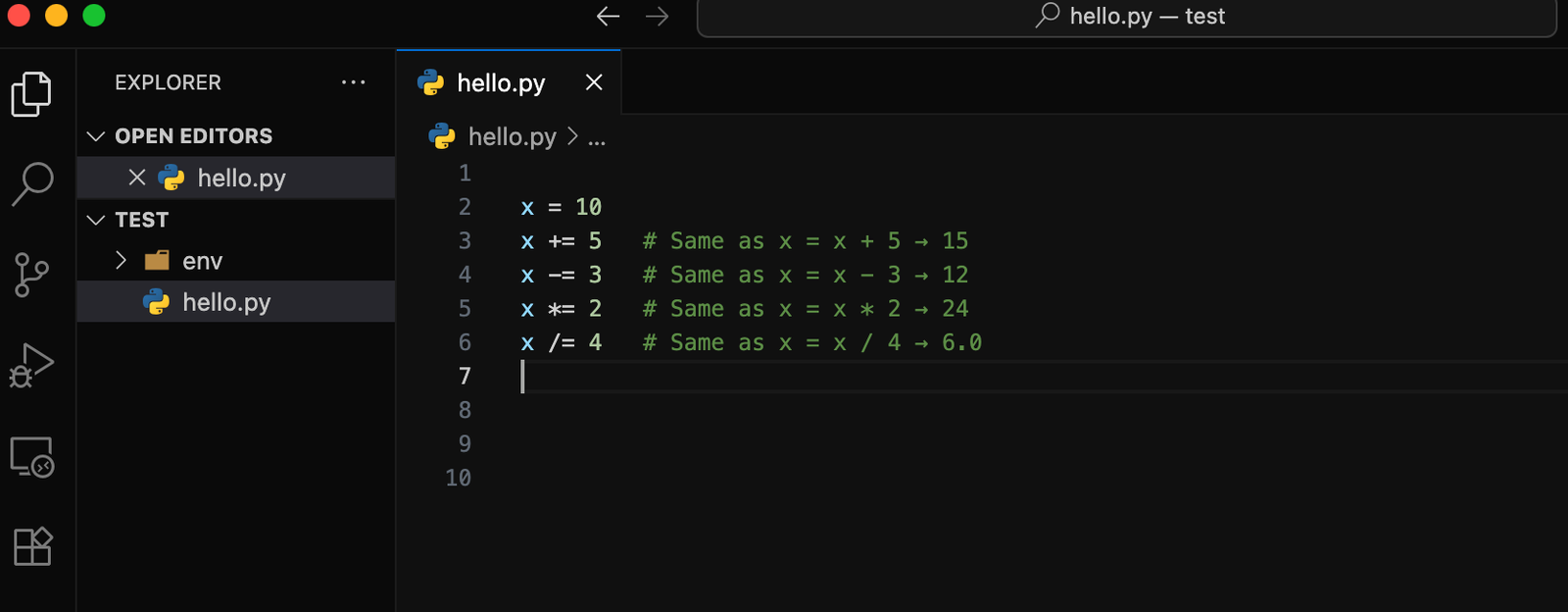
🔹 4. Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are shortcuts for updating variables.
🔹 5. Combining Operators in Expressions
You can mix different operators to create more complex expressions.
🔹 Exercises for Beginners
Try these in a new Python file (lesson3.py):
- Create two variables
a = 15 and b = 4. Print their:- sum
- difference
- product
- quotient (both
/ and //) - remainder
- exponent (
a ** b)
- Check if
25 is greater than 10 and less than 30. - Suppose you have
x = 7. Use assignment operators to:- Add 3
- Multiply by 2
- Subtract 4
- Challenge: Write a small program that checks if a person can vote.
- Variable:
age - Condition: age must be
>= 18 - Print
True if eligible, False if not.
🎯 Recap
In this lesson, you learned:
✅ Arithmetic operators for calculations
✅ Comparison operators for checking conditions
✅ Logical operators for combining conditions
✅ Assignment operators for quick updates
Next up: Lesson 4 – Strings in Python (working with text, string methods, and formatting). ✨
💼 Need a Developer?
I'm Kingsley Odume, a Django, Flask, and FastAPI developer with experience building SaaS platforms, APIs, and modern web apps.
If you're a recruiter or business owner looking for a reliable software developer, let's connect!
🚀 Hire Me








